| [1] Li D, Yan Y, Yu L, et al. Procaine Attenuates Pain Behaviors of Neuropathic Pain Model Rats Possibly via Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3. Biomolecules AND Therapeutics. 2016;24(5): 489-494. [2] Pozeg P, Palluel E, Ronchi R, et al. Virtual reality improves embodiment and neuropathic pain caused by spinal cord injury. Neurology. 2017;89(18):1894-1903.[3] López Chiriboga AS, Cheshire WPJr. Trigeminal Neuralgia Following Lightning Injury. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2017;31(4):e7.[4] Galánarriero I, Serranomuñoz D, Gómezsoriano J, et al. The role of Omega-3 and Omega-9 fatty acids for the treatment of neuropathic pain after neurotrauma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1859(9 Pt B). [5] Taha O, Opitz T, Mueller M, et al. Neuropathic pain in experimental autoimmune neuritis is associated with altered electrophysiological properties of nociceptive DRG neurons. Exp Neurol. 2017;():.[6] Ran R, Gu J, Fu J, et al. The role of the GABA-A receptor of the adjacent intact dorsal root ganglion neurons in rats with neuropathic pain. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2014;74(4): 405-414.[7] Tan AM, Samad OA, Dibhajj SD, et al. Virus-Mediated Knockdown of Nav1. 3 in Dorsal Root Ganglia of STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats Alleviates Tactile Allodynia. Mol Med. 2014;21(1):544-552.[8] Jia T, Rao J, Zou L, et al. Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Curcumin Inhibits Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Involving the P2Y12 Receptor in the Dorsal Root Ganglia. Front Neurosci. 2018;11:755.[9] Lagares A, Li HY, Zhou XF, et al. Primary sensory neuron addition in the adult rat trigeminal ganglion: evidence for neural crest glio-neuronal precursor maturation. J Neurosci. 2007;27(30):7939-7953. [10] 杨悦橙,马柯.卫星胶质细胞参与神经病理性痛的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2013,19(6):2766-2770.[11] Hanani M. Satellite glial cells in sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia: In search of function. Brain Res Rev. 2010;64(2):304-327.[12] Liu FY, Sun YN, Wang FT, et al. Activation of satellite glial cells in lumbar dorsal root ganglia contributes to neuropathic pain after spinal nerve ligation. Brain Res. 2012;1427(1):65-77.[13] Nascimento DS, Castro-Lopes JM, Moreira Neto FL. Satellite glial cells surrounding primary afferent neurons are activated and proliferate during monoarthritis in rats: is there a role for ATF3? PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e108152.[14] Ji RR, Berta T, Nedergaard M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain. 2013;():S10-S28.[15] Yoon SY, Robinson CR, Zhang H, et al. Spinal astrocyte gap junctions contribute to oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. J Pain. 2013;14(2):205-214.[16] 焦晓翠,张会然,张璇,等.卫星胶质细胞对外周神经元作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2014;30(5):612-614.[17] Eugenin EA, Basilio D, Sáez JC, et al. The Role of Gap Junction Channels During Physiologic and Pathologic Conditions of the Human Central Nervous System. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012;7(3):499-518. [18] Cui Y, Masaki K, Yamasaki R, et al. Extensive dysregulations of oligodendrocytic and astrocytic connexins are associated with disease progression in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. J Neuroinflammation. 2014;11:42..[19] Hanani M. Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: from form to function. Brain Res Rev. 2005;48(3):457-476.[20] Hanani M, Huang TY, Cherkas PS, et al. Glial cell plasticity in sensory ganglia induced by nerve damage. Neuroscience. 2002;114(2):279-283.[21] Vit JP, Jasmin L, Bhargava A, et al. Satellite glial cells in the trigeminal ganglion as a determinant of orofacial neuropathic pain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2006;2(4):247-257.[22] Ohara PT, Vit JP, Bhargava A, et al. Evidence for a role of connexin 43 in trigeminal pain using RNA interference in vivo. J Neurophysiol. 2008;100(6):3064-3073.[23] Hanani M. Intercellular communication in sensory ganglia by purinergic receptors and gap junctions: implications for chronic pain. Brain Res. 2012;1487(17):183-191.[24] Gu Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, et al. Neuronal soma-satellite glial cell interactions in sensory ganglia and the participation of purinergic receptors. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010;6(1):53-62.[25] Suadicani SO, Cherkas PS, Zuckerman J, et al. Bidirectional calcium signaling between satellite glial cells and neurons in cultured mouse trigeminal ganglia. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010; 6(1):43-51.[26] Weick M, Cherkas PS, Härtig W, et al. P2 receptors in satellite glial cells in trigeminal ganglia of mice. Neuroscience. 2003; 120(4):969-977. [27] Villa G, Fumagalli M, Verderio C, et al. Expression and contribution of satellite glial cells purinoceptors to pain transmission in sensory ganglia: an update. Neuron Glia Biol. 2010;6(1):31-42.[28] Ceruti S, Fumagalli M, Villa G, et al. Purinoceptor-mediated calcium signaling in primary neuron-glia trigeminal cultures. Cell Calcium. 2008;43(6):576-590.[29] Takeda M, Takahashi M, Matsumoto S. Contribution of the activation of satellite glia in sensory ganglia to pathological pain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2009;33(6):784-792.[30] Katagiri A, Shinoda M, Honda K, et al. Satellite glial cell P2Y12 receptor in the trigeminal ganglion is involved in lingual neuropathic pain mechanisms in rats. Molecular Pain. 2012;8(1):23.[31] Tang X, Schmidt TM, Perezleighton CE,et al. Kir4. 1 is Responsible for the Native Inward Potassium Conductance of Satellite Glial Cells in Sensory Ganglia. Neuroscience. 2010; 166(2):397-407. [32] Bellot-Saez A, Kã©Kesi O, Morley JW, et al. Astrocytic modulation of neuronal excitability through K+ spatial buffering. Neurosci Biobehav R. 2017;(77):87-97.[33] Vit JP, Ohara PT, Bhargava A, et al. Silencing the Kir4.1 potassium channel subunit in satellite glial cells of the rat trigeminal ganglion results in pain-like behavior in the absence of nerve injury.J Neurosci. 2008;28(16):4161-4171.[34] Scholz J, Woolf CJ. The neuropathic pain triad: neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10(11):1361.[35] Ren K, Dubner R. Neuron-glia crosstalk gets serious: role in pain hypersensitivity. Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology. 2008;21(5):570.[36] Milligan E, Watkins L. Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2008;10(1): 23.[37] Schöbitz B, Voorhuis DA, De Kloet ER.Localization of interleukin 6 mRNA and interleukin 6 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci.1992;136(2):189-192. [38] Vallières L, Rivest S. Regulation of the genes encoding interleukin-6, its receptor, and gp130 in the rat brain in response to the immune activator lipopolysaccharide and the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1beta. J Neurochem. 1997;69(4):1668-1683.[39] Chiang CY, Wang J, Xie YF, et al. Astroglial glutamate- glutamine shuttle is involved in central sensitization of nociceptive neurons in rat medullary dorsal horn.J Neurosci. 2007;27(34):9068-9076.[40] Fonseca LL, Monteiro MA, Alves PM, et al. Cultures of rat astrocytes challenged with a steady supply of glutamate: new model to study flux distribution in the glutamate-glutamine cycle. Glia. 2005;51(4):286-296.[41] Chiang CY, Li Z, Dostrovsky JO, et al. Glutamine uptake contributes to central sensitization in the medullary dorsal horn. Neuroreport. 2008; 19(11):1151-1154. [42] Sung B, Lim G, Mao J. Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats.J Neurosci. 2003;23(7):2899-910.[43] Kung LH, Gong K, Adedoyin M, et al. Evidence for Glutamate as a Neuroglial Transmitter within Sensory Ganglia. PLoS One.2013; 8(7):e68312. [44] Ohara PT, Vit JP, Bhargava A,et al.Gliopathic pain: when satellite glial cells go bad.Neuroscientist. 2009;15(5):450-463.[45] Mclachlan EM, Jänig W, Devor M, et al. Peripheral nerve injury triggers noradrenergic sprouting within dorsal root ganglia. Nature.1993;363(6429):543-546.[46] Chung K, Kim HJ, Na HS, et al. Abnormalities of sympathetic innervation in the area of an injured peripheral nerve in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett.1993;162(1-2): 85-88.[47] Rubin G, Kaspi T, Rappaport ZH, et al. Adrenosensitivity of injured afferent neurons does not require the presence of postganglionic sympathetic terminals. Pain.1997; 72(1-2): 183. [48] 闫栋,蒋劲,张德仁.背根节交感芽生与神经病理性疼痛关系的总结和思考[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2010;16(3):169-171.[49] Shinder V, Govrin-Lippmann R, Cohen S, et al. Structural basis of sympathetic-sensory coupling in rat and human dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury. J Neurocytol.1999;28(9):743-761.[50] Deng YS, Zhong JH, Zhou XF. Effects of endogenous neurotrophins on sympathetic sprouting in the dorsal root ganglia and allodynia following spinal nerve injury. Exp Neurol. 2000;164(2):344-350.[51] Ramer MS, Thompson SW, Mcmahon SB. Causes and consequences of sympathetic basket formation in dorsal root ganglia. Pain. Pain. 1999;Suppl 6:S111-120. [52] Zhou XF, Deng YS, Chie E, et al. Satellite-cell-derived nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3 are involved in noradrenergic sprouting in the dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury in the rat. Eur J Neurosci.1999;11(5): 1711-1722.[53] Jones MG, Munson JB, Thompson SW. A role for nerve growth factor in sympathetic sprouting in rat dorsal root ganglia. Pain.1999;79(1):21.[54] Asensio VC, Campbell IL. Campbell IL. Chemokines in the CNS: plurifunctional mediators in diverse states. Trends Neurosci.1999;22(11):504.[55] Deiva K, Geeraerts T, Salim H, et al. Fractalkine reduces N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced calcium flux and apoptosis in human neurons through extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20(12):3222-3232.[56] Yang JL, Bo X, Li SS,et al.Gabapentin reduces CX3CL1 signaling and blocks spinal microglial activation in monoarthritic rats. Molecular Brain, 5, 1(2012-05-30). 2012, 5(1):1-12. [57] Verge GM, Milligan ED, Maier SF, et al. Fractalkine (CX3CL1) and fractalkine receptor (CX3CR1) distribution in spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia under basal and neuropathic pain conditions. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20(5):1150-1160.[58] Clark AK, Staniland AA, Malcangio M. Fractalkine/CX3CR1 signalling in chronic pain and inflammation. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12(10):1707-1714.[59] Milligan E, Zapata V, Schoeniger D, et al. An initial investigation of spinal mechanisms underlying pain enhancement induced by fractalkine, a neuronally released chemokine. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;22(11):2775-2782.[60] Staniland AA, Clark AK, Wodarski R, et al. Reduced inflammatory and neuropathic pain and decreased spinal microglial response in fractalkine receptor (CX3CR1) knockout mice. J Neurochem. 2010;114(4):1143-1157.[61] Souza GR, Talbot J, Lotufo CM, et al. Fractalkine mediates inflammatory pain through activation of satellite glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(27):11193-11198. |
.jpg)
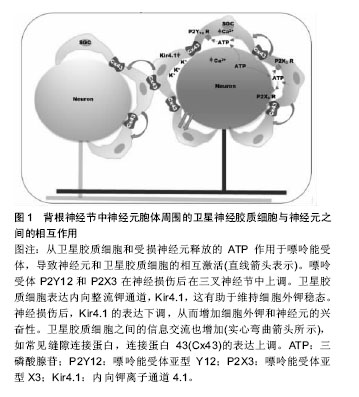
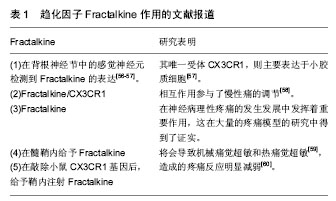
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
经病理性疼痛(neuropathic pain,NPP):是由躯体感觉神经系统的损伤或疾病而直接造成的疼痛,它属于一种慢性疼痛,疼痛表现为自发性疼痛、痛觉过敏、异常疼痛和感觉异常等临床特征。按痛觉冲动的发生部位,疼痛可以分为躯体痛、内脏痛和神经性疼痛。#br#
交感芽生:周围神经损伤后,形态学观察到正常在背根神经节内部支配血管的交感性缩血管神经纤维开始芽生,新生的交感纤维弥撒分布在背根节中神经元之间,并在一些神经元大细胞胞体周围形成篮状结构或者在卫星胶质细胞间隙中形成洋葱皮样结构。背根神经节交感芽生现象现已被认为和神经病理性疼痛有着直接的关系。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
经病理性疼痛(neuropathic pain,NPP):是由躯体感觉神经系统的损伤或疾病而直接造成的疼痛,它属于一种慢性疼痛,疼痛表现为自发性疼痛、痛觉过敏、异常疼痛和感觉异常等临床特征。按痛觉冲动的发生部位,疼痛可以分为躯体痛、内脏痛和神经性疼痛。#br#
交感芽生:周围神经损伤后,形态学观察到正常在背根神经节内部支配血管的交感性缩血管神经纤维开始芽生,新生的交感纤维弥撒分布在背根节中神经元之间,并在一些神经元大细胞胞体周围形成篮状结构或者在卫星胶质细胞间隙中形成洋葱皮样结构。背根神经节交感芽生现象现已被认为和神经病理性疼痛有着直接的关系。